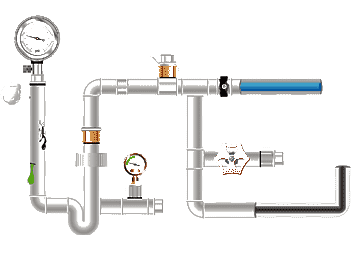
A valve is a device used to control the direction, pressure, and flow of a fluid in a fluid system. It is a device that makes or stops the flow of media (liquid, gas, powder) in piping and equipment and controls its flow.
The valve is a control component in the pipeline fluid conveying system, which is used to change the passage section and the flow direction of the medium, and has the functions of diversion, cut-off, throttling, check, diversion or overflow and pressure relief. Valves used for fluid control range from the simplest shut-off valve to various valves used in extremely complex automatic control systems. Valves for industrial pipelines. It can be used to control the flow of various types of fluids such as water, steam, oil, gas, mud, various corrosive media, liquid metals and radioactive fluids. The working pressure of the valve can be from 0.0013MPa to 1000MPa ultra-high pressure, and the working temperature can be c-270°C ultra-low temperature to 1430°C high temperature.
The control of the valve can adopt a variety of transmission methods, such as manual, electric, hydraulic, pneumatic, turbine, electromagnetic, electromagnetic hydraulic, electrohydraulic, pneumatic hydraulic, spur gear, bevel gear drive, etc.; can be driven by pressure, temperature Under the action of sensing signals in other forms, it acts according to predetermined requirements, or simply opens or closes without relying on sensing signals. The valve relies on drive or automatic mechanism to make the opening and closing parts lift, slide, swing or rotate. Movement, thereby changing the size of its channel area to achieve its control function.

Classification by function and use
1 Shut-off valve
This type of valve is used for opening and closing. It is permanently installed on the inlet and outlet of cold and heat sources, the inlet and outlet of equipment, and branch lines of pipelines (including standpipes). It can also be used as a water discharge valve and air release valve. Common shut-off valves include gate valves, globe valves, ball valves and butterfly valves.
Gate valves can be divided into bright rods and dark rods, single gates and double gates, wedge gates and parallel gates, etc. The closing tightness of the gate valve is not good, and it is difficult to open the large-diameter gate valve; the size of the valve body is small in the direction of water flow, the flow resistance is small, and the nominal diameter span of the gate valve is large.
Globe valves are divided into three types: straight-through type, right-angle type and straight-through type according to the flow direction of the medium, and there are bright rods and dark rods. The closing tightness of the globe valve is better than that of the gate valve, the valve body is long, the flow resistance is large, and the maximum nominal diameter is DN200.
The spool of the ball valve is a ball with a hole. When the plate moves the valve stem so that the opening of the ball is facing the axis of the pipeline, it is fully open, and when it is turned 90°, it is fully closed. The ball valve has a certain adjustment performance and is more tightly closed.
The valve core of the butterfly valve is a circular valve plate, which can rotate along the vertical shaft perpendicular to the pipeline axis. When the plane of the valve plate is consistent with the axis of the pipe, it is fully open; when the plane of the gate plate is perpendicular to the axis of the pipe, it is fully closed. Butterfly valve body length is small, flow resistance is small, and the price is higher than gate valve and globe valve.
This type of valve is used to prevent the medium from flowing backwards. It uses the kinetic energy of the fluid itself to open itself and closes automatically when it flows in the reverse direction. It is always installed at the outlet of the water pump, the outlet of the steam trap and other places where the reverse flow of fluid is not allowed. There are three types of check valves: swing type, lift type and wafer type. For the swing check valve, when fluid can only flow from left to right, it will automatically close when it flows in the opposite direction. For the lift check valve, when the fluid flows from left to right, the valve core is lifted to form a passage, and when the fluid flows in the reverse direction, the valve core is pressed against the valve seat to be closed. For the wafer check valve, when the fluid flows from left to right, the valve core is opened to form a passage, and when the fluid flows in the opposite direction, the valve core is pressed to the valve seat to be closed. Installation, small size, light weight, compact structure.
3 Control valve
The pressure difference between the front and back of the valve is constant. When the opening of the ordinary valve changes in a wide range, the flow rate changes little, but when it reaches a certain opening degree, the flow rate changes sharply, that is, the regulation performance is not good. The regulating valve can change the stroke of the spool to change the resistance of the valve according to the direction and magnitude of the signal, so as to achieve the purpose of regulating the flow of the valve.
Regulating valves are divided into manual regulating valves and automatic regulating valves, and manual or automatic regulating valves are divided into many types, and their regulating performance is also different. Automatic regulating valves include self-operated flow regulating valves and self-operated differential pressure regulating valves.
4 Vacuum class
Vacuum categories include vacuum ball valves, vacuum flapper valves, vacuum inflation valves, pneumatic vacuum valves, etc. Its function is that in the vacuum system, the components of the vacuum system used to change the direction of the air flow, adjust the size of the air flow, and cut off or connect the pipeline are called vacuum valves.
5 Special purpose category
Special purpose categories include pigging valves, vent valves, drain valves, exhaust valves, filters, etc.
The exhaust valve is an indispensable auxiliary component in the pipeline system, and is widely used in boilers, air conditioners, oil and gas, water supply and drainage pipelines. It is often installed at commanding heights or elbows to remove excess gas in the pipeline, improve the efficiency of pipeline use and reduce energy consumption.
Classified by main parameters
1 Vacuum valve
Refers to a valve whose working pressure is lower than the standard atmospheric pressure.
2 Low-pressure valve
Refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN ≤ 1.6Mpa.
3 Medium pressure valve
Refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN of 2.5Mpa, 4.0Mpa, 6.4Mpa.
4 High pressure valve
Refers to the valve whose nominal pressure PN is 10.0Mpa~80.0Mpa.
5 Ultra-high pressure valve
refers to the valve with nominal pressure PN ≥ 100.0Mpa.
Classified by working temperature
1 Ultra-low temperature valve
Used for valves with medium working temperature t<-101°C.
2 Normal temperature valve
Used for valves with medium working temperature -29°C<>
(3) Medium temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature of 120°C<>
(4) High temperature valve: used for valves with medium working temperature t>425°C.
<>
<>
Classified by drive mode
<>
1 Small diameter valve
<>
A valve with a nominal diameter DN≤40mm.
<>
<>
2 Medium diameter valve
<>
A valve with a nominal diameter DN of 50-300mm.
<>
<>
3 Large diameter valve
<>
A valve with a nominal diameter DN of 350-1200mm.
<>
<>
4 Extra-large diameter valve
<>
A valve with a nominal diameter DN≥1400mm.
<>
<>
<>
Classified by structural features
<>
1 Cut-off shape
<>
The closing member moves along the center of the valve seat; such as a globe valve.
<>
<>
2 Plug and spherical
<>
The closing member is a plunger or a ball, which rotates around its own center line; such as plug valves, ball valves.
<>
<>
3 Gate shape
<>
The closing member moves along the center of the vertical seat; such as gate valve, gate, etc.
<>
<>
4
Swing shape
<>
The closing member rotates around the axis outside the valve seat; such as swing check valve, etc.
<>
<>
5
Butterfly
<>
T
he disc of the closing member rotates around the axis in the valve seat; such as butterfly valve, butterfly check valve, etc.
<>
6 Slide valve shape
<>
<>
The closing member slides in a direction perpendicular to the channel. slippery.
<>
<>
<>
<>
<>
<>
Classified by connection method
<>
1 Threaded connection valve
<>
The valve body has internal or external threads, and is connected to the pipe thread.
<>
<>
2 Flange connection valve
<>
The valve body has a flange and is connected to the pipe flange.
<>
<>
3 Welding connection valve
<>
The valve body has a welding groove and is welded with the pipeline.
<>
<>
4 Clamp connection valve
<>
The valve body has a clamp, which is connected with the pipe clamp.
<>
<>
5 Ferrule connection valve
<>
It is connected with the pipe by ferrule.
<>
<>
6 Wafer connection valve
<>
A connection form in which the valve and the pipes at both ends are directly clamped together by bolts.<>
<>
<>
<>
<>
Classified by body material
<>
1 Metal material valve
<>
Its valve body and other parts are made of metal material. Such as cast iron valves, cast steel valves, alloy steel valves, copper alloy valves, aluminum alloy valves, lead alloy valves, titanium alloy valves, Monel alloy valves, etc.
2 Non-metallic material valves
The valve body and other parts are made of non-metallic materials. Such as plastic valves, enamel valves, ceramic valves, FRP valves, etc.
<>













 Baowu Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.
Baowu Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd not only improve product production and sales services, but also provide additional value-added services. As long as you need, we can complete your specific needs together.